Humanitarian OSM Team/Open Mapping Hub Eastern and Southern Africa/Data Quality Approach
An Approach for Improving OpenStreetMap Data Quality in Eastern and Southern Africa
Background
In the Eastern and Southern Africa region, OpenStreetMap has gained popularity in recent years, and its use has been steadily increasing. OSM data is being used by a variety of organizations, including government agencies, NGOs, and private companies, for various purposes such as disaster response, urban planning, and resource management. The Eastern & Southern Africa region is experiencing rapid urbanization, which has led to an increased demand for accurate and up-to-date map data.
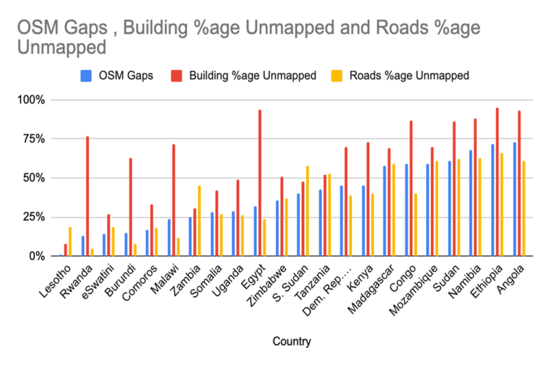
Despite the growing use of OSM in the region, the quality of the data remains a challenge. This is due to factors such as a lack of data coverage, low data accuracy, and limited community engagement among others identified in Top 10 data quality aspects. There is a need to improve the quality of the data in order to fully realise the potential of OSM in the region. In this document, we outline a strategy for identifying and addressing issues with OpenStreetMap data quality and we hope this document will be useful to other mapping communities addressing similar issues in other contexts and regions.
Objectives
The key objectives of this strategy include these highlighted below;
- Increase the number of active mappers in the region: to build a vibrant and engaged community of mappers who can contribute to improving the quality of OSM data in the region.
- Improve data accuracy: increase the accuracy of OSM data in the region, particularly in areas where the data is incomplete or outdated.
- Increase map edits in unmapped areas: expand the coverage of OSM data in the region, particularly in rural and remote areas that are currently underrepresented on the map.
- Enhance community engagement: foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for the quality of OSM data in the region among the local communities.
- Increase awareness, trust and use of OSM data: increase the awareness and use of OSM data in the region, particularly among government agencies, NGOs, and private companies.
Our Approach
Increase the number of active mappers in the region
A directory of these active mappers for each country can be accessed through OSMStats by Pascal. To increase the number of active mappers in the region, the Eastern and Southern Africa Hub will be organizing a variety of training programs that cover the basics of mapping, data validation, and community engagement. These programs will include workshops, webinars, and online training modules that are designed to be accessible to people with different levels of experience. In addition, engaging with local communities will be critical to building a vibrant and engaged mapping community in the region. This is the heart of our Spatial People Network program that is aimed at achieving this objective.
To increase the number of mappers in the region, we plan to organize mapping events, recognize active mappers in the region, host meetups and workshops, and collaborate with local organizations to identify and map priority areas. This approach will not only help to improve the quality of OSM data but also foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for the data among local communities, and organizations that contribute and use OSM data. These programs are currently being implemented through the Spatial People Network program.
Improve data accuracy and quality
What Is Data Quality
The quality of data in OpenStreetMap is highly contextual; therefore, different uses of OpenStreetMap data require different metrics of quality depending on the context in which the data is going to be used. For the purpose of this document, we define OpenStreetMap data quality as fit-for-purpose that confirms minimum requirements by the users.
Data Quality Assurance
To improve data accuracy, regular data quality assessments will be conducted to identify areas where the data is incomplete, inaccurate, or out of date. This will involve both manual and automated data validation processes that will help to identify and correct errors in the data. The results of these assessments will be used to prioritize mapping efforts and guide community engagement activities.
Data quality assessment will be based on the Top 10 data quality aspects that HOT is focusing on and the core impact area use cases & data quality metrics that are being defined as the basis of measuring quality of OSM data.
Quality Assurance Tools
There are several OSM data quality assurance tools that can be used to improve the accuracy and completeness of OSM data. Our tools of choice include:
1. JOSM Editor: The JOSM Editor is a desktop application that provides more advanced editing features than other OSM editing tools. It also includes plugins that can be used to perform more extensive data validation checks, such as detecting overlapping buildings and missing and depreciated tagging information.
2. Osmose: Osmose is a web-based tool that checks OSM data for potential errors and provides a list of issues that need to be addressed. It includes checks for data completeness, consistency, and accuracy, such as missing tags, overlapping features, and incorrect road classifications.
3. OSMCha: OSMCha is a web-based tool that allows mappers to review and validate OSM edits made by themselves and others. It includes filters that can be used to identify and review specific edits, such as those made by new mappers or in specific geographic areas.
4. Changeset discussion: OpenStreetMap contributors can have a discussion about an edit directly in OpenStreetMap associated with that changeset. This discussion is public, which allows for contributor collaboration.
5. MapRoulette: MapRoulette is an open-source platform for crowdsourcing and managing microtasks related to OpenStreetMap data. It is a user-friendly tool that allows users to create, manage, and complete small mapping tasks that are typically too tedious to be addressed through traditional mapping methods.
6. HeiGIT: Information on OpenStreetMap activity or contributor level in each country.
7. Disaster Ninja: Current State of OSM Data Quality in the region.
Mapping Events (Campaign, Activations and Mapathons)
To ensure data quality during mapping events, these are some of the approaches we will take;
Remote Mapping
For all hub led remote mapping efforts;
- Ensure that there are no overlapping active projects on the tasking manager. Reference Tasking Manager Onboarding and Project creation guidelines.
- Utilize public GPS traces from platforms like OSM GPS Tracks, Mapillary and Strava to identify best object alignment for Imagery Offsets.
- Reference OSM Wiki Map Features and the HOT Data Models for feature tagging guidelines.
- Monitor local changeset discussion and Tasking Manager discussion. If there is a discussion about your mapping activity, provide appropriate and timely responses.
- Live Validation: Identify data quality issues in new data immediately and provide quick feedback to mappers. This OpenStreetMap diary explains the concept. Ensure that projects are fully validated and archived after mapping.
- Inform the mapping project coordinator immediately for any questionable edits from participants. You can refer to this problem user escalation document.
- Ensure all changeset discussion and Tasking Manager discussion are documented or responded to.
Field Mapping
For all hub-led field mapping projects;
- Prepare public documentation on the Wiki OpenStreetMap.
- Reference OSM Wiki Map Features and the HOT Data Models for feature tagging guidelines.
- Validation to check for naming conventions, tag completeness and positional accuracy that can be done in JOSM.
- Monitor local changeset discussion. If there is a discussion about our mapping activity, provide appropriate and timely responses.
Enhance community engagement
As a collaborative project, OSM relies on the contributions of its community members to create and maintain accurate and up-to-date maps. As OSM continues to grow, with new users joining every day, community engagement is essential for welcoming and supporting new users, providing guidance and resources to help them get started, and encouraging them to contribute to the project in meaningful ways. The hub will take the following steps to achieve this goal;
- Mapping Challenges and Contests: Organizing mapping challenges and contests to incentivize community members to contribute to the map. These challenges are focused on specific areas or features, and prizes are awarded to the best contributors. Mapping challenges can help improve the quality of OSM data by encouraging community members to map areas that may have been overlooked.
- Training and Workshops: Conduct training and workshops to educate new and existing community members on mapping techniques, best practices, and data quality standards. This approach can help improve the quality of OSM data by providing community members with the knowledge and skills they need to map accurately and consistently.
- Local Events: Facilitate community members to hold regular meetings, organize mapping parties, and work on specific mapping projects in their community. Local mapping groups can help improve the quality of OSM data by leveraging local knowledge and expertise to map accurately and consistently.
- Advocacy and Round tables: Promote OSM to others, including individuals, organizations, and government agencies, to encourage more people to use and contribute to the project. Advocacy can help raise awareness and generate interest in OSM, leading to more community engagement and a better map.
- Documentation: Contribute to the OSM documentation, such as the wiki, to help others learn about mapping techniques, tagging standards, and community guidelines.
Conclusion.
Improving OpenStreetMap (OSM) data quality in Eastern and Southern Africa is essential for effective decision-making, planning, and development in the region. Community engagement, training, and data validation efforts can enhance OSM data accuracy, completeness, and timeliness. Collaboration between local and international stakeholders, including government agencies, civil society organizations, universities, and the private sector, is crucial.
Ongoing investment and sustained efforts to ensure that OSM data remains up-to-date and relevant to the needs of local communities are necessary. Good-quality OSM data enables better-informed decision-making, supports disaster response and risk reduction efforts, promotes sustainable development, and enhances access to essential services. By adopting a collaborative approach to mapping and data quality, the Hub can make OSM a valuable resource for various purposes in Eastern and Southern Africa.
We're always looking for ways to improve this approach. Please share your feedback with us