JA:経路探索
英語版の記事の内容が分かる方は、翻訳の完成にご協力ください。このウィキの翻訳方法についての説明をお読みください。
現時点では、誰もこの記事の翻訳に取り組んでいないようですので、あなたが取り組めます。
経路探索(ルーティング、ナビゲーション)サービスは人々がある場所から別の場所へたどり着くのを手助けしてくれます。 OpenStreetMap データは車、徒歩、自転車及び乗馬といった多くのモードで経路探索のための情報を含んでいます。 OpenStreetMap データを使っている多くのオフライン、組み込み型及びWebベースの経路探索サービスがあります。
このページでは、開発者向けに新しい経路探索アプリケーションの開発や配布ができるソフトウェアのアドバイスや、経路探索エンジンをより良くするために使われる OpenStreetMap データの詳細なキーを提供しています。数多くのメーリングリストも利用可能です。
エンドユーザー向け: 経路探索ソフトウェア
List of OSM based Services#Routing も参照してください
- simply on the OSM homepage (blog post with description)
- Routing/online routers – There are many websites that use OpenStreetMap data to provide online route planners; those with global support are featured below.
- Routing/offline routers – Furthermore several options exist for installing offline navigation software on your handheld device or laptop.
- Navigation apps are available for Android, Apple iOS, Java ME (J2ME) and Openmoko. For other mobile platforms see JA:ソフトウェア#Mobile Devices.
- Example: Routing from Hères to Thère, France
マッパー向け: 地図データを改良する
経路検索ソフトウェアがうまく機能するようにするには、その裏にあるデータの品質が良くなければなりません。これは、接続されているべきウェイが実際に接続されており、一方通行の道はタグ付けされ、右折・左折の制限もマッピングされているといったことを意味します。そのためには、Map Features をよく理解し、特に 経路探索のためのOSMタグ を読んで経路検索に使われるタグを理解する必要があります。
MapDust でバグを修正する
MapDust に登録されているバグの多くは、iOS や Android のナビゲーションアプリによって直接追加されたもので、地図データの改善すべき点を探すのに役立ちます。一方通行の道路や右折・左折制限に関するバグは、それとわかるようにマークされています。
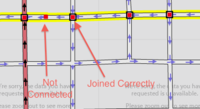
小さな領域の中に "poor routing" や "other"のバグがたくさん表示される場合、ウェイ同士が適切に接続されていない可能性があります。Potlachcでは、ウェイを選択するとすべてのノードがハイライトされます。ノードが大きな正方形になっているならば、それは他のウェイと接続されています。OSMのデータの品質を上げるには、WayCheck が生成したレポートも利用できます。
注意: Mapdustを使用するときは "Hide bugs with default text" のチェックを外してみてください。ナビゲーションアプリを使うときにデフォルトの文言を変更しないユーザも多いからです。
速度データ
最も速く着くルートを検索できるようにするために、maxspeed=* を入れるようにしてください。これは特に、国や車両の種類による道路の種類ごとの推測される速度制限と実際の速度制限が異なる場合に役に立ちます。
- 注: ITO World は、速度制限の抜けを見つける のに役立つさまざまなサービスを提供しています。
最高速度が意味を持たないこともよくあります - #Average speed をご覧ください。
修正をチェックする
地図のエラーを修正した後は、使っている経路検索エンジンに地図の修正版が反映されるまで待たなければなりません。この遅延は、
- データベースからアップデートを取得する頻度
- 内部データベースの更新にかかる時間
によります。 OSRMの場合、通常は1日に2回データがアップデートされ、アップデートを処理するのに10-12時間かかります。そのため、保存した修正箇所が OSRM で使えるようになるにはトータルで10〜24時間かかるということになります。
開発者向け
デスクトップ・サーバーソフトウェア
Java:
- Traveling salesman という経路探索アプリケーションはユーザインタフェース以外の全ての基本部分で使われている osmNavigation ライブラリを含んでいます。全ての重要な部分はプラグイン経由で交換することができます。
- OpenTripPlanner site is a multi-modal trip planner supporting OSM data. OTP Deployer makes it easy to deploy your own routing instance.
- GraphHopper is an open source routing engine for road networks written in Java. Fast and memory efficient (for Android, iOS, desktop and server).
- BRouter focuses on bike routing and features elevation awareness, alternatives, fully configurable routing profiles and offline routing initially written for Android, but has now also a web api
- Cruiser は地図と経路探索のアプリケーションです。
C/C++:
- Gosmore
- MoNav
- Navit
- Open Source Routing Machine
- Routino Flexible router with user selectable routing preferences.
- Valhalla ([1])
C#:
- IMORTIS(Intermodal Transport Routing Informations-System) is an approach to route/optimize transport routes via different vehicles using a optimized A* Algorithm
- OsmSharp Library for routing and transportation optimization problems.
- Simple Map Routing Demo routing program (using optimized double A* Algorithm) with SQLite and OSM uploader.
Scala
- osm_routing super-simple plain Dijkstras
Ruby
- Mormon ruby version of pyroutelib
Python
- PyrouteLib routing engine behind Pyroute
- SimpleOsmRouter simplest possible router
モバイル機器のソフトウェア
C/Java:
- OsmAnd OSM Map, POI and Routing (car/bike/foot, online&offline) for Android
- ZANavi Android
- Navit Linux, Windows and portable devices
- GraphHopper Open Source routing library for Desktop, Android and iOS.
- BRouter focuses on bike routing and features elevation awareness, alternatives, fully configurable routing profiles and offline routing for Android
- OpenTripPlanner_(Android) is an Android app for multi-modal trip planning using any OpenTripPlanner server
- Cruiser は地図と経路探索のアプリケーションです。
ライブラリ/開発ツール
Libraries focused on OSM Routing can be found at Develop/Frameworks. Here some general libs:
- DGLib Directed Graph Library は Grass のベクターネットワークツールです(最短経路、巡回セールスマン、 isodistances、 Steiner trees、 Addons)
- Graphserver is a webservice providing shortest-path itineraries on TIGER/line road maps, and public transport data in the General Transit Feed Specification format
- osm4routing is a command-line tool for parsing OSM data into a routing graph.
- pgRouting - PostGIS-based routing engine. Special tool osm2pgrouting for importing OSM data to internal graph structure. Works directly on top of SQL database tables.
- Libosmscout offers simple, high-level interfaces to offline rendering and routing functionalities based on OpenStreetMap data
- Spatialite Spatialite has its own routing engine VirtualNetwork and a spatialite_osm_net tool for building a routable network directly from OSM data. Routing can use either Dijkstra or A* algorithm.
- GraphHopper routing engine with Java API.
- ffwdme.js is a JavaScript toolkit that aims to bring interactive GPS driving directions to the mobile browser.
- Valhalla is a free, open-source routing service that lets you integrate routing and navigation into a web or mobile application.
プロトコル:
- The default-protocol is the API v0.6 spoken by the main servers. If can contain all data there is in OSM. Get Planet.osm dump.
- There is also a compressed but limited OSM Mobile Binary Protocol.
経路探索の条件
道路の種別
The order of values for the highway-tag ordered by assumed speed is:
| 種別 | 説明(主に西欧でいえること) |
|---|---|
| motorway | Usually the maxspeed can be kept for long distances, but these roads can be sensitive to long traffic jams. Usually forbidden for slow traffic (pedestrians, cyclists, agricultural, ...) |
| trunk | Similar to motorways, but these roads can have level crossings, so the stretches where the maximum speed can be reached are shorter. Best avoided when using slow vehicles (sometimes forbidden, depending on the local legislation). |
| primary | Connecting roads between cities, towns and villages. The classification depends mostly on the importance of the areas they connect. This is often also reflected in the number of lanes and the general traffic throughput, but the speed for these classifications is mostly comparable. Usually around 90-100 km/h in the countryside, and 50 (or even 30) km/h when crossing a residential center. |
| secondary | |
| tertiary | |
| motorway_link | Used for on- and off-ramps or complete motorway junctions. Reachable speed depends a lot on curvature, usually around 60-90 km/h |
| trunk_link | In contrast to motorway junctions, these link roads are often very short pieces (f.e. allowing one to turn right without stopping at a traffic light). The speed on these road pieces is very slow, as these often need to give way to the other traffic. |
| primary_link | |
| secondary_link | |
| tertiary_link | |
| unclassified | These roads usually connect farms, isolated houses and small hamlets through the countryside to bigger residential areas. Due to lack of traffic signs, they often have a speed limit way faster than can be driven safely. Speed on a well-maintained but unfamiliar unclassified road will rarely exceed 50 km/h. |
| residential | Residential roads are found in a residential area, so usually have a speed limit of 50 km/h to 30 km/h, with a lot of traffic calming features. |
| living_street | Living streets are streets where slow traffic has absolute right-of-way. The speed limit is normally around 20 km/h. Through-going traffic is absolutely discouraged (and often impossible). |
| service | Service roads are usually found on private property or parking lots. The driver has to pay attention to manoeuvring vehicles, and must wait often. |
| track | Tracks are roads of agricultural purpose. They usually connect fields to farms. The surface sometimes makes them inaccessible for regular cars, or at least limits the speeds to a very slow pace. Tracks should always be avoided for through-going traffic. |
| pedestrian | Pedestrian roads are normally forbidden for motorised vehicles, but can be allowed on certain hours (f.e. early in the morning), or for certain purposes (like delivering goods to shops). Even when allowed, only pedestrian speed is advisable. Cycling can also be forbidden on pedestrian highways. |
This is highly country specific and rather useless without country specific values. For example in Germany primary roads allow 100km/h both legally and as a realistic speed while minor motorway_link(s) are built to allow a recommended speed of 60 km/h, only major motorway_links allow a realistic speed of 80 or 100. For more information see OSM_tags_for_routing/Maxspeed#Additional_information_for_selected_countries
車線
道路の車線数は OSM で直接タグ付けされ、平均速度(最短経路)及び燃料消費(最も効率的な経路)に関して大きな影響を持っています。There is no simple mapping to speed unfortunately, in many cases more lanes only indicate more congestion.
道路の状態
Other factors, in our case more difficult to measure, which determine the average speed are the width of pavement, condition of the network (roadworks, surface type and surface smoothness - especially in ex-USSR), Levels of Service (LOS), minimal radius curve, banked turns, visibility based on curves and gradients, etc.
OpenStreetMap において、このモデルは速度に関するデータが無い経路(例: highway=unclassified)にとっては興味深いものになるでしょう。
勾配
Same as curves, inclines may decrease the speed of traffic. In winter of when lots of hgv is present the hindrance is also on the descending way. While some inclines are explicitly tagged, in some cases utilization of additional informations such as ele=* and height elevation profile from DEM data could prove useful.
湾曲(Sinuosity)
turning radius=* も参照してください
In some studies about the accessibility [2] develop models that assume a certain speed of travel depending on the degree of sinuosity of the track and certain characteristics of this one. By means of the sinuosity index (observed line distance/expected line distance ) for every section it is possible to obtain a speed estimated according to the degree of winding of the road and type of route. This needs to take into account the visibility around corners (determined by vegetation, embankments, cuttings, cliffs,...) and road width. The model is more precise if the excessively large arcs are avoided provided that a long curve can be equal to many small curves along a way, giving similar values of sinuosity for both routes. Some countries use these values to divide sections of roads and put speed limits (but this is not usual).
On the other hand, geographical approaches like that of the space syntax presuppose that, in urban environments, pedestrians and drivers are influenced at the moment of choosing theirs paths for the visibility of the route. In this respect a pedestrian who moves, for example, from the point A to the point B will select principally wide and rectilinear streets, squares or avenues with a wide visual field, avoiding crossed by winding and narrow streets, even when the latter route is somewhat shorter.
横断歩道、交差点、車線変更
Certain cost should be assumed for:
- crossing higher-class roads
- changing to and from lower-class roads
- u-turns
- lane changes
平均速度
OpenStreetMap data will need average/realistic speed values for routing.
- maxspeed:practical=* is a rejected but nevertheless used proposal to tag estimated average speed values (with the possibility to specify day/night/rush hour values) in areas where official speed limits are largely meaningless and road/track type information insufficient to derive meaningful travel speed estimates.
- Speedcollector is a currently defunct service to collect real-world measurements, while it might be possible to derive average speed per way from stored tracks.
- Global Statistical Speed Matrix is a proposed concept (no current signs of life?) to extract speed information from NMEA/GPX tracks and store them efficiently in a database to make collected data useful for routing purposes.
経路検索のヒントになる他のタグの一覧
自転車
- ハイキングを参照
ハイキング
特別な合意を必要とするその他の経路検索の障害物やその他の条件
- crossing=* - 歩行者などの横断歩道、速度が低下
メーリングリスト
以下のメーリングリストが経路探索に関連しています
- osm-routing 'ベクターデータでの経路探索についての議論。特に OSM データに関して'
- osm-accessibility このMLでは、障害のある人々にとって特に有用な、あらゆる種類のアクセシビリティに関する提案、およびタグの使用法について議論されています。このデータを元に、特別なマップを作成することができるでしょう。
関連項目
- JA:経路探索のためのOSMタグ - 経路検索時に使うことができるものとして、どんなデータが OpenStreetMap に格納されているか
- CartoType, cartotype.com
- Rollstuhlfahrer-Routing - 車椅子向け経路探索のドイツのプロジェクト
- Routing problems - Are there any problems that can't be solved using least-cost routing? Do we have any suggestions for solving those problems?
- Routing profiles - Which categories of people want to generate routes, and what are their specific needs? What weights should we use when a 'horse who's scared of traffic lights but likes walking in the forest' asks for a route? How do we choose the best route for a cyclist with slick tires and no lights at night?
- Sample driving instructions
- TIGER fixup - Fixing routing in the U.S. Starting with basic interstate routes: TIGER fixup/250 cities
- Train routing- How can we do routing on public transport networks, and other scheduled services?
- LoroDux - 視覚障碍者向けのモバイル機器向けの歩行者経路探索
- Taxi to... - a funny approach to long-distance routing comparison
- Video: Google Tech Talk - Peter Sanders - Fast Route Planning
- Leaflet Routing Machine