Key:lanes
| Description |
|---|
| Total number of traffic lanes available for motorised traffic. |
| Group: highways |
| Used on these elements |
| Useful combination |
| See also |
| Status: de facto |
| Tools for this tag |
|
Use the lanes=* key to tag how many traffic lanes there are on a highway (described on this page) or other features like a piste or running track (described on the respective pages). To tag individual lanes of a road, see the article about the lanes suffix. Count excludes cycle lanes and motorcycle lanes that do not permit a motor vehicle. For tagging cycle lanes see cycleway=*. For tagging motorcycle lanes see motorcycle=* or lanes.
Note that it is valid to tag lanes count also in case where lanes are not marked with paint on the surface[1]
Description
The lanes=* key should be used to specify the total number of ![]() lanes of a road.
lanes of a road.
The following lanes should be included:
- General purpose
![Wikipedia [W]](/w/images/2/24/Wikipedia-16px.png) traffic lanes suitable for vehicles wider than a motorbike.
traffic lanes suitable for vehicles wider than a motorbike. ![Wikipedia [W]](/w/images/2/24/Wikipedia-16px.png) Bus lanes, that are reserved for public service vehicles (PSV), for example buses and taxis. Additionally to the total number of lanes, consider to tag the number of lanes reserved for PSV with lanes:psv=*. Similarly, one may do similar with lanes:bus=*, lanes:taxi=* etc.
Bus lanes, that are reserved for public service vehicles (PSV), for example buses and taxis. Additionally to the total number of lanes, consider to tag the number of lanes reserved for PSV with lanes:psv=*. Similarly, one may do similar with lanes:bus=*, lanes:taxi=* etc.![Wikipedia [W]](/w/images/2/24/Wikipedia-16px.png) High-occupancy vehicle lanes (sometimes also called carpool lanes, commuter lanes, express lanes, transit lanes). The number of such lanes could be tagged using lanes:hov=*.
High-occupancy vehicle lanes (sometimes also called carpool lanes, commuter lanes, express lanes, transit lanes). The number of such lanes could be tagged using lanes:hov=*.- Lanes that are available to traffic at certain restricted times, for example during the rush hour, indicated by variable message signs. These lanes are called
 spitsstroken(nl) in the Netherlands and Belgium, and
spitsstroken(nl) in the Netherlands and Belgium, and  temporäre Standstreifen(de) in Austria, Germany and Switzerland. The "smart lanes" concept in the United States is similar, repurposing the roadway's shoulder=*. [1]
temporäre Standstreifen(de) in Austria, Germany and Switzerland. The "smart lanes" concept in the United States is similar, repurposing the roadway's shoulder=*. [1] - Longer slip-roads, for example on motorways and other fast major roads. Turning lanes for minor roads are not normally included. See turn=* for further details about tagging turning lanes.
And the following lanes should be excluded:
- Minor slip roads without a deceleration/acceleration lane, i.e. the main road is wider only because of the intersecting road.
- Lanes dedicated and marked for parking. Use parking:lane=* to provide information on if and how cars park.
- Bicycle lanes. Use the tag cycleway=lane for those.
- Emergency
![Wikipedia [W]](/w/images/2/24/Wikipedia-16px.png) shoulder lanes. See shoulder=* for further details.
shoulder lanes. See shoulder=* for further details.
If the number of lanes changes it is necessary to split the OSM way. This should be done as soon as:
- a new lane has started (regardless of width), or
- a lane has finished disappearing (usually a merge with another lane)
width:lanes:start/end can be used to mark that a lane gradually gets narrower.
Remark for data consumers
Many ways have not yet been tagged with the total number of lanes at all points, but only with the number of through lanes of a longer section. Therefore, data consumers can mostly treat the lanes tag as a minimum rather than an exact number.
If there are no marked lanes, the keys width=* or width:carriageway=* can be used.
Extended tagging
Lanes in different directions
If the lanes on a two way road are not distributed evenly between the driving directions, the keys lanes:forward=* and lanes:backward=* can be used in addition to the lanes tag. The key lanes:forward=* hereby refers to lanes which direction is equal to the direction of the OSM way, and lanes:backward=* to the opposite direction.
The lanes=* tag is widely misused to mean the lanes in each direction rather than the total lanes. If the mapper chooses to describe the forward and backward lanes, this potential ambiguity is avoided.
lanes:both_ways=* can be used for lanes which allow traffic in both directions, e.g., passing and center turn lanes.
See below for some examples of the usage of those keys.
Lanes reserved for specific vehicles
The number of lanes which are reserved for specific types of vehicles can be tagged by using the key lanes and adding a suffix that indicates the transport mode from the key access=*, e.g. lanes:bus=1 for a single lane reserved for buses. If it is necessary to specify the direction of those lanes, add the suffix :forward or :backward like in the previous section, i.e. lanes:taxi:forward=1 refers to single lane reserved for taxis in the same direction as the OSM way.
NOTE! The lanes:*=* key type can only be used to indicate the number of lanes that are reserved for a specific transport type on a way. It does not and cannot specify which lanes a transport type is restricted to.
If, for example, on a three lane motorway, heavy-good vehicles are restricted to the rightmost lane only, lanes:hgv=1 will not express that meaning! It simply means that hgv vehicles have one lane of the motorway reserved for them, but it doesn't specify which one.
Restrictions for vehicles can be tagged using the :lanes suffix and tagging scheme, e.g. hgv:lanes=no|no|yes would restrict heavy-good vehicles to the rightmost lane.
Restrictions that only apply at certain times and days
For lanes that are restricted for parts of the day only, use the additional lanes conditions tag to indicate when the conditions apply. For example: lanes:bus:conditional=* or lanes:psv:conditional=*. See Conditional restrictions for more details.
No lane markings
Many narrow, cobblestone and rural roads do not have lane markings. Also, in some places, even broader roads that function as 4-laned highways may not have lane markings. To signify that a road has no lane markings, it is recommended to use an explicit tag like lane_markings=no or similar instead of an odd value for the lanes=* key like 0, 1.5 or none because the latter is ambiguous and may not be processed correctly by data consumers.[2]
For narrow roads (without marked lanes) in particular, it is very useful to tag the width=*/width:carriageway=* of the road, see below.
Narrow roads
There exist roads with no marked lanes, which are two-way roads but without marked lanes and so narrow, that vehicles must slow down to pass each other. This can be tagged with narrow=yes. It is strongly recommended in such a case to tag the width of the carriageway using width=* or better width:carriageway=* (Note: do not mistake this with maxwidth=*). If the width varies a lot, the minimum width of the carriageway should be specified. If it is not possible or reasonable to determine the exact width, use an estimation and tag additionally source:width=estimated, e.g. as follows:
width=4 source:width=estimated
Sometimes on narrow roads ![]() passing places exists, which allow vehicles to pass each other (see examples). They can be tagged using highway=passing_place. The lanes-count is not affected by them.
passing places exists, which allow vehicles to pass each other (see examples). They can be tagged using highway=passing_place. The lanes-count is not affected by them.
Examples
|
Lanes available for motorised traffic | ||
|---|---|---|
| Photo | Tags | Remarks |

|
lanes=1 | A bridge with sign only allowing 1 vehicle at a time. |

|
lanes=2 | A two-way residential road with two lanes. Consider additional tagging with parking:lane=*. |

|
lanes=2 on the first line lanes=2 on the second line Each direction individually |
A dual 2-lane highway, represented by two ways as there is a physical divider between them (each with oneway=yes). |

|
lanes=2 lane_markings=no |
Two-way road without marked lanes, but it has 1 lane in each direction. White markings on sides are delineators indicating boundary of the road. These lines do not, however, mark the individual lanes, only the edge of the road, so lane_markings=no should be used. |

|
lane_markings=no and optionally: width=4 |
A narrow two-way road without marked lanes and with an estimated width of four metres. It is not qualifying for tagging as road with two lanes as there is not enough space for vehicles to comfortably pass each other. |

|
lanes=1 oneway=yes |
A one-way road which has only 1 lane. The parking bays do not count as a lane. |

|
lanes=1 oneway=yes oneway:bicycle=no cycleway=opposite_lane |
A road which is one-way for cars, but has a Contraflow Lane for bikes. lanes=1 because the cycleway does not count as a lane. |

|
lanes=1 oneway=alternating |
Some bridges on two-way roads only have one lane. You must give way if there are vehicles coming in the opposite direction. Requires either oneway=alternating/reversible |

|
highway=passing_place (on the node) | A passing place on a road. |

|
lanes=8 | A road with four lanes in either direction plus a flush median (the crosshatched area in the middle). If lanes:forward=* and lanes:backward=* are omitted, the eight lanes are assumed to be distributed evenly between the forward and backward directions. In New Zealand, a flush median is considered a travel lane (see below). |

|
lanes=3 lanes:forward=1 lanes:backward=1 lanes:both_ways=1 turn:lanes:both_ways=left |
A road with one lane in either direction plus a center turn lane. The center turn lane can be used by traffic going in either direction at any time to turn at any point along the lane. This configuration is common in some countries but rare or nonexistent in others. |

|
lanes=5 lanes:forward=3 lanes:backward=2 Assuming the OSM way runs from left to right |
A road with five lanes, whereas three lanes run in forward direction, i.e. in the same direction as the OSM way. The turning lanes should be tagged using turn=* on the way. |

|
lanes=3 lanes:bus:conditional=1 @ (Mo-Fr 07:00-19:00) |
A road with three lanes where the rightmost lane is dedicated to buses at the given time. The merging of the leftmost lane should be tagged with the key turn=*. See the article Conditional restrictions for an detailed explanation of the :conditional suffix. |
|
Lanes available for non motorised traffic | ||

|
highway=cycleway lanes=2 |
A cycleway with two marked lanes. (Attention, as described above and seen in the example: Lanes#Crossing_with_a_designated_lane_for_bicycles bicycle lanes only counts for tag lanes=* if the cycleway has a physical separation and it is therefore mapped as a separated OSM way) |

|
leisure=track lanes=8 |
A track with 8 marked lanes. |

|
piste:type=nordic piste:lanes=2 |
A piste route with two classic xc lanes. Avoid just lanes=* since the piste often shares way with a highway=* for which the number of lanes might not be applicable. |
For further examples see: User:Martinq/Lane_examples
The following example shows a motorway with two links.

|
lanes=3 | |
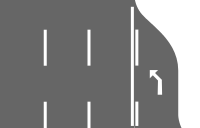
|
lanes=4 turn:lanes=none|none|none|merge_to_left | |

|
lanes=3 (lanes=1 on ramp roads) | |
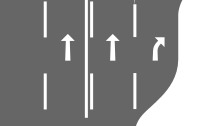
|
lanes=4 turn:lanes=none|through|through|slight_right | |

|
lanes=3 turn:lanes=none|none|through;slight_right destination:lanes=A|A|B | |

| ||

|

|
lanes=4 turn:lanes=through|through|through|slight_right |
Assumptions
If for a two way road only the total lane count is tagged and this number is even, it is assumed that the lanes are allocated evenly to both driving directions (e.g. lanes=6 assumes the road has 3 lanes for each direction).
Although it is advisable to always add the lanes tag to roads with lanes, as usual data will be sometimes missing. It is usually reasonable for data consumer to try guessing. Data consumer may make any guesses, but following assumptions often work well:
| Tag(s) | Assumed lane-count two way |
Assumed lane-count one way |
Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| highway=residential highway=tertiary highway=secondary highway=primary |
2 | 1 | If the actual number of lanes is equal to the given assumption, the lane count is usually not tagged. |
| highway=unclassified highway=service highway=track highway=path |
1 | 1 | If the actual number of lanes is equal to the given assumption, the lane count is usually not tagged. |
| highway=motorway highway=trunk |
These should usually be mapped as two separate ways
See the article Dual carriageway for a detailed explanation. |
2 or more | The actual number of lanes should always be tagged. |
Displaying the number of lanes
- To view the number of lanes in JOSM, a Lane and road attributes style is available. Alternatively, its routes plugin can be used with this lane coloring example.
- These Maperitive lane rules renders highway widths, lanes and offsets based on lanes=* and placement=*.
- OpenStreetMap detailed overlays generates a road overlay with lanes, cycleways, parking, and sidewalks rendered at higher zooms (16+). A slippy map version is available online.
Related tags
- width=*/width:carriageway=* for tagging the width of the carriageway
- source:width=* for specifying the source of the width
- access=* for transport modes and additional access restrictions
- parking:lane=* for parking lanes
- turn=* for turning lanes
- highway=passing_place for passing places
- shoulder=* for highway shoulders (often serving as an emergency stopping lane)
See also
- Tagging of individual lanes and their properties
- Relation for linking the lanes of two road segments
- Abandoned proposal for turnlanes relation to describe complex geometry of lanes, supported by JOSM "turnlanes" plugin
- Abandoned proposal for lane tagging system using different delimiters
- Proposal for tagging the number of tracks of railways
- Proposal for the suffix :both_ways
- Proposed_features/lanes_General_Extension -
:lanes- Specify properties for each lane of a way - Discussion on tagging
- Discussion on tagging, before the cleanup of this article in April 2012
- ↑ see discussion from June 2019 on tagging mailing list ( https://lists.openstreetmap.org/pipermail/tagging/2019-June/046002.html ) and discussion on German forum from September 2019 ( https://forum.openstreetmap.org/viewtopic.php?id=67330 ), additionally several remarks on the discussion page. The change to explicitly mentioning "marked" was made 2014 as result of another discussion in the German forum but not from anywhere else.
- ↑ https://lists.openstreetmap.org/pipermail/tagging/2019-June/046002.html