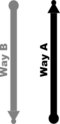Bicycle

|
| Description |
| Bicycle and cycleway features |
| Group |
| Tags |
|
This page lists some possible options for how to enter and tag bicycle and cycleway related data into OSM. Having good quality cycleway data allows routing software to choose the way that best suits cyclists.
Cycle features
OSM distinguishes between cycle lanes and cycle tracks. A cycle lane lies within the roadway itself (on-road), whereas a cycle track is separate from the road (off-road). Tracks are typically separated from the road by e.g. curbs, parking lots, grass verges, trees, etc.
There are two ways to model cycle tracks. One possibility is to draw separate ways along the roadway which are tagged as highway=cycleway. The alternative is to add a cycleway=track tag to the existing way. Both methods each have their pros and cons. Notably, a separately tagged cycleway generally allows to capture more detail, while adding a single tag to an existing way takes much less time and in many cases can be as accurate. Both methods are in use today, and there is discussion about when to prefer which method.
The tables below with many examples and pictures are for right-hand drive countries.
Cycle lanes in bidirectional motor car roads
A lane marked on a portion of a carriageway (UK), roadway or shoulder (USA), designated for cyclist use.
| Ref | Context | Photo | OSM | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1a | 
|
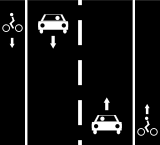
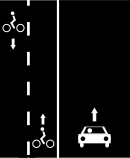
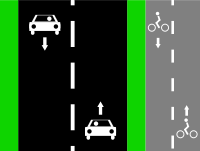
Cycle lanes on left and right sides of the road.
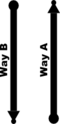
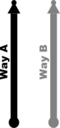
Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway=lane or Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway:left=lane + cycleway:right=lane or Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway:both=lane | ||
| L1b | 
|
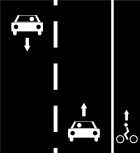
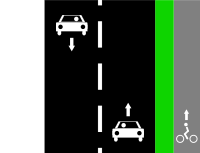
Bidirectional cycle lane on right side of the road.
Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway:right=lane + cycleway:right:oneway=no or Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway=lane (note this can't be distinguished from L1a) | ||
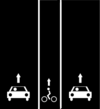
| L2 | Oneway cycle lane on right side of the road only.
Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway:right=lane (nb: bikes can use the normal highway on the left side) |
Cycle lanes in oneway motor car roads
| Ref | Context | Photo | OSM | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 
|
Cycle lanes on left and right sides of the oneway road.
Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + cycleway=lane + oneway:bicycle=no or Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + cycleway:left=lane + cycleway:right=lane + oneway:bicycle=no |
370646853 | ||
| M2a | 
|
Oneway cycle lane on right side and same direction of the oneway road.
Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + cycleway:right=lane or |
|||
| M2b | Oneway cycle lane on left side and same direction of the oneway road.
Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + cycleway:left=lane or |
cycleway:left=lane 53°16′40.58″ N, 9°04′17.62″ W | |||
| M2c | Oneway cycle lane in the direction as the oneway road, between driving lanes.
Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + lanes=2 + cycleway=lane (note that this tagging is ambiguous with a cycle lane that is on the right or left side of the road) |
||||
| M2d | Bidirectional cycle lane on left side of the oneway road.
Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + oneway:bicycle=no + cycleway:left=lane + cycleway:left:oneway=no
|
619210833 | |||
| M3a | 
|
Oneway contraflow cycle lane on left side and opposite direction of the oneway road. Cyclists in one direction use lane together with other vehicles, in opposite one they have a dedicated lane.
Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + oneway:bicycle=no + cycleway:left=lane + cycleway:left:oneway=-1 |
132400917 | ||
| M3b | Oneway contraflow cycle lane on right side and opposite direction of the oneway road. Cyclists in one direction use lane together with other vehicles, in opposite one they have a dedicated lane.
Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + oneway:bicycle=no + cycleway:right=lane + cycleway:right:oneway=-1 |
||||
| M4 | Oneway cycle lane on right side of separated oneway roads.
Way A: same as M2a Way B: same as M2a |
||||
| Alternative tagging for less accurate traces / aerials.
Way A: same as L1a |
|||||
| M5 | Oneway cycle lane on right side of a separated oneway road.
Way A: same as M2a |
||||
| Alternative tagging for less accurate traces / aerials.
Way A: same as L2 |
Cycle tracks
Road (UK) or path (USA, Canada) dedicated to cyclists on separate right of way.
| Ref | Context | Photo | OSM | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 
|
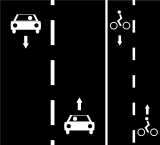
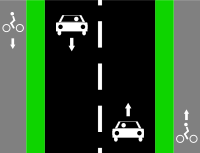
Cycle tracks on left and right sides of the road.
Way A: highway=*[1] + bicycle=use_sidepath if usage of cycle track is compulsory | ||
| (Alternative solution with a single way, also useful when the track position is not known) | ||||
| T2 | 
|
Bidirectional cycle track right side of the road.
Way A: highway=*[1] + bicycle=use_sidepath if usage of cycle track is compulsory | ||
| (Alternative solution with a single way, also useful when the track position is not known)
Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway:right=track + cycleway:right:oneway=no | ||||
| T3 | Bidirectional cycle track right side of the one way road.
Way A: highway=*[1]+ oneway=yes + bicycle=use_sidepath if usage of cycle track is compulsory | |||
| (Alternative solution with a single way, also useful when the track position is not known)
Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + cycleway:right=track + oneway:bicycle=no | ||||
| T4 | Oneway cycle track on right side of the road.
Way A: highway=*[1] + bicycle:forward=use_sidepath if usage of cycle track is compulsory | |||
| (Alternative solution with a single way, also useful when the track position is not known)
Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway:right=track (nb: bikes can use the normal highway on the left side) |
Miscellaneous
| Ref | Context | Photo | OSM | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Cycling opposite to the oneway car traffic without dedicated lane/track (in some countries only).
Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + oneway:bicycle=no | |||
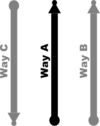
| S2 | Cycle track on left side and cycle lane on right side of the road.
Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway:right=lane + bicycle:backward=use_sidepath if usage of cycle track is compulsory | |||
| Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway:left=track + cycleway:right=lane | ||||
| S3 | If sidewalks are mapped as a tag on the main highway: | |||
| Cycle tracks on left and right sides of the road and sidewalks.
If sidewalks are mapped as a tag on the main highway: Way A: highway=*[1] + bicycle=use_sidepath if usage of cycle track is compulsory | ||||
| If sidewalks are mapped as separate ways:
Way A: highway=*[1] + bicycle=use_sidepath if usage of cycle track is compulsory Way B: highway=path + bicycle=designated + oneway=yes + foot=designated + segregated=yes Way C: highway=path + bicycle=designated + oneway=yes + foot=designated + segregated=yes | ||||
| If sidewalks are mapped as separate ways without highway=path:
Way A: highway=*[1] + bicycle=use_sidepath if usage of cycle track is compulsory Way B: highway=cycleway + oneway=yes + foot=designated + segregated=yes Way C: highway=cycleway + oneway=yes + foot=designated + segregated=yes | ||||
| S4 | Easiest
Way A: highway=*[1] + cycleway=track + segregated=yes + foot=designated | |||
| Cycle tracks on left and right sides of the road and the sidewalks/footways.
Way A: highway=*[1] + bicycle=use_sidepath if usage of cycle track is compulsory Way B: highway=cycleway + oneway=yes + foot=designated + segregated=yes Way C: highway=cycleway + oneway=yes + foot=designated + segregated=yes | ||||
| Alternative solution with 5 ways in OSM:
Note that this variant is controversial as there is no physical separation between the cycleway and the footway. Use another variant if possible. Way A: highway=*[1] + bicycle=use_sidepath if usage of cycle track is compulsory Way B: highway=cycleway + oneway=yes | ||||
| S5 | (footway + cycleway with different surfaces) | Easiest, ignore differences in type of paved surface
highway=path + segregated=yes + foot=designated + bicycle=designated + surface=paved | ||
| Use cycleway:surface=* and footway:surface=*
highway=path + segregated=yes + foot=designated + bicycle=designated + surface=paved + cycleway:surface=asphalt and footway:surface=paving_stones | ||||
| Tag it as two separate ways:
Note that this variant is controversial as there is no physical separation between the two ways. Use another variant if possible. Way A: highway=footway + surface=paving_stones | ||||
| S6 | Steps with bicycle ramps can be tagged see ramp=*, possible bicycle friendly value can be:
ramp:wheelchair=yes | |||
| S7 | Way designated for both cyclists and pedestrians, without separate spaces. Such combined footway+cycleway can be standalone or a sidewalk next to a road (in such case also footway=sidewalk is applicable)
highway=footway/highway=cycleway/highway=path + bicycle=designated + foot=designated + segregated=no + surface=* | |||
| S8 | Footway not designated as a cycleway but where cycling is legal (for example in a park where rules allow this) |
Cycle lanes and bus/taxi lanes
| Ref | Context | Photo | OSM | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | Cycle lanes on left and right sides of the road with a bus/taxi only lane.
Proposal (no consensus): Using the suffix for Lanes: Note: the suffix | |||
| B2 | Cycle lanes on left and right sides of the road after a bus/taxi only lane in right side.
Proposal (no consensus): Way A: highway=*[1] + lanes=3 + lanes:forward=2 + lanes:bus:forward=1 + busway:right=lane + cycleway=lane | |||
| B3 | Cycle lane on left side of the road and a shared cycle lane with a bus/taxi lane in right side.
Way A: highway=*[1] + busway:right=lane + cycleway:left=lane + cycleway:right=share_busway | |||
| B4 | Cycle track shared with a bus/taxi track in right side of the road.
Proposal (no consensus): Way A: highway=service + service=bus + oneway=yes + cycleway:right=share_busway Way B: | |||
| B5 | Cycle lane shared with a bus/taxi lane on right side of the road (in some countries only).
Proposal (no consensus): Way A: highway=*[1] + lanes=4 + lanes:bus:forward=1 + busway:right=lane + cycleway:right=share_busway | |||
| B6 | 
|
Cycle lane shared with a bus/taxi lane in opposite direction of the oneway road.
Proposal (no consensus): Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + oneway:bicycle=no + cycleway:left=share_busway + cycleway:left:oneway=-1 + busway=opposite_lane or Way A: highway=*[1] + oneway=yes + oneway:bus=no + oneway:bicycle=no + cycleway:left=share_busway + cycleway:left:oneway=-1 + busway=lane |
All pictures are available in both .png and .svg files in the wiki repository (use .png when text is present).
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 1.24 1.25 1.26 1.27 1.28 1.29 1.30 1.31 1.32 1.33 1.34 1.35 1.36 1.37 1.38 1.39 1.40 1.41 any type of motor car roads in the class highway=* like primary/secondary/tertiary/unclassified/residential/etc.
Cycle streets and bicycle roads
A cycle street is a street designed for bicycle with low motor traffic. Currently this exists in Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Finland, the Netherlands, Norway, Slovenia and Switzerland. In all cases, there are specific traffic signs, each with their own implications. Have a look at the cyclestreet=* wiki page for more details.
The concept is closely related to bicycle_road=*, which only exist in Germany.
Add cyclestreet=yes, don't change highway=*.
Pedestrian streets
highway=pedestrian + (if needed) bicycle=yes
Off-road and outdoor
Outside of cities and dense populated areas most cycling routes are mapped using highway=track when the way is also used by large motorized vehicles (agricultural, forestry, emergency vehicles...) or highway=path when not intended for motorized vehicles (rather pedestrians, horses...). While both imply bicycle=yes in most areas of the world, it is difficult for bicycle routers to suggest them as routes because a wide range of conditions (path surface, incline,..) can make them unsuitable for some or all types of bicycles.
Some additional tags that should be used to indicate suitability of such ways for bicycles:
- surface=*
- smoothness=*
- tracktype=*
- mtb:scale=*
- incline=*
See also Mountain biking.
On-road cycling (cycle-friendly streets)
Consider using the following key/values to indicate cycle friendly streets. These tags are objective and useful for detecting ways friendly for cyclists.
| Key | Value | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| maxspeed | speed limit | Roads with lower speed limits tend to be less crowded by cars. |
| source:maxspeed | country_code:rural/country_code:urban/sign/… | Always tag the source of the maxspeed limit! |
| surface=*
tracktype=* smoothness=* |
For cyclists there is a very significant difference between surface=asphalt and surface=sand/surface=grass_paver/surface=unhewn_cobblestone, larger than for pedestrians or cars. Tagging for smoothness and track type quality is two other means to specify the surface quality of a road or a path. | |
| traffic_calming=* | Traffic calming features is a good way to limit the speed of motor vehicles and making the street safer for cyclists. | |
| lanes=* | total number of marked lanes making up the way | Single lane wide roads with low speed limits tend to be low-stress routes (but may increase stress for cyclists that want to cycle fast) |
| width | width of road in metres | Indicate a wide single lane road or a squeeze point |
| shoulder | no/yes/left/right/both | Indicate the presence of a shoulder |
| cycleway | asl | Advanced stop line, also known as bike boxes in North America |
Bicycle restrictions
| Key | Value | When to use |
|---|---|---|
| bicycle | yes | Where bicycles are permitted, overriding default access (such as to motorways that permit bicycles, as can often be found in western parts of North America) |
| bicycle | designated | Where a way has been specially designated (typically by a government) for bicycle use |
| bicycle | use_sidepath | Where cycling on the main road is legally discouraged because of a parallel compulsory cycle track. Check with local laws. |
| bicycle | optional_sidepath | Where cycling on the main road is legally allowed but a parallel (optional) cycle track exists. |
| bicycle | no | Where bicycles are not permitted, ensure this is indicated. Note that carrying or pushing bicycles may be still accepted[1][2]. |
| bicycle | permissive | Where bicycles do not have a legal right-of-way, but the land owner has indicated that bicycles are allowed. |
| bicycle | destination | Where bicycles have a legal right-of-way, but only if their destination is within that street or area. |
| bicycle | dismount | Where cycling is not allowed on short sections of signposted cycle routes, though "walk and push" (push the bicycle, while dismounted from it) is allowed. |
| oneway:bicycle | yes/no | Use oneway:bicycle=* to identify roads where the oneway rules for cyclists differ from the general oneway restriction. If there is a contraflow lane, see ref M3a and M3b above. If tagging an object where bicycles are the only permitted vehicles, a simple oneway=* should be used instead. |
See also OSM tags for routing/Access-Restrictions for the default restrictions by highway type (and country-specific rules).
All values: access=*.
For restrictions on speed pedelecs and electric bicycles, see the corresponding wiki pages.
Routes
Individual sections of road/street/path may collectively form an overall route with official signage.
These should be represented by creating a Relation, as follows:
plus the type of network:
- network=lcn - local cycle network routes
- network=rcn - regional cycle network routes
- network=ncn - national cycle network routes
Only official routes, i.e. those signed on-street and/or published on maps by a local authority, should be entered into OSM. Informal recommendations, such as suggested routes published on general websites, do not form official infrastructure, and as such are not objective.
The use of lcn=* / rcn=* / ncn=* on a per-Way basis is deprecated and should no longer be used.
Separation from other road users
Where a path is shared-use, i.e. for use by both cyclists and pedestrians, if the path is split, e.g. by a white line, the segregated=* tag should be used:
| segregated=yes | Cyclists and pedestrians are separated, e.g. with a white line. |
| segregated=no | No separation between cyclists and pedestrians. |
Note that the segregation tag has nothing to do with segregation with motor vehicles. For that, use the separation tag:
Separation from motor vehicles
Where a cycle track/lane is within a road and separated from other vehicles, e.g. protected (segregated) bike lanes, this should be specified using the new separation=* tag.
This enables specifying:
- The type of separation
- Which side of the cycleway the separation is on
| separation=* | Used when the cycleway is mapped as a separate line (but is still built within the roadspace). |
| cycleway:separation=* | Used when the cycleway is mapped as an attribute of the road line. |
Barriers and obstructions
Cycle infrastructure may incorporate various obstructions such as bollards, barriers, gates, and non-flush kerbs.
Because they can cause delays - or even entirely prevent users of larger cycles from using a path, it is important that such obstructions are mapped.
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| barrier=cycle_barrier | For mapping chicanes. The maximum available physical width, or individual spacing/opening/overlap widths, can be specified. |
| barrier=bollard | For bollard(s) within a path. |
| barrier=gate | For a gate. |
| kerb=no | For when there is no kerb between sections of path/road, resulting in the cyclist having to stop/dismount. By constrast, kerb=flush can be used to declare explicitly that the kerb, i.e. no barrier. |
| highway=steps | Steps obviously require cyclists to dismount. If there is a wheeling channel/ramp, add ramp:bicycle=yes. See example above. |
Cycle parking
Cycle parking is important for the security of bicycle users. Facilities can range from individual stands, lockable units, or even a large dedicated cycle park building.
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| amenity | bicycle_parking |
You should also ideally include the type, capacity (number of cycles) and whether covered. Full details are on the bicycle_parking page.
Facilities
Where there are facilities to rent/hire bicycles, use:
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| amenity | bicycle_rental |
| service:bicycle:rental | yes |
For shops that sell cycles and equipment:
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| shop | bicycle |
| service:bicycle:retail | yes |
For air pumps which can be used to refill bicycle tyres:
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| amenity | compressed_air |
| compressed_air | yes |
| service:bicycle:pump | yes |
For a do-it-yourself (DIY), self repair station:
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| amenity | bicycle_repair_station |
| service:bicycle:diy | yes |
For a vending machine selling inner tubes:
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| vending | bicycle_tube |
For street furniture or devices for cyclists that are intended to make waiting at esp. traffic lights more comfortable (known as "cyclist footrests", "leaning rails" or "bike rests"):
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| highway | cyclist_waiting_aid |
Bicycle counters
- Bicycle counters (with an optional display, i.e. totem/barometer with clock)
Bicycle clubs and associations
Online services using OSM
Cartography/tiles
- OpenCycleMap - a rendering project for bikers
- CyclOSM - a free rendering project for every cyclist
Interactive maps
- Bicycle tags map - slippy map with bicycle related OSM tags
- Waymarked Trails - a map showing bicycle and mountain bike routes
- flosm cycle map - cycle map with routes
- CicloMapa - cycle maps, POIs and metrics for Brazilian cities
- Amenagements-cyclables by GeoVelo - provides local statistics for France and a global basemap clearly highlighting a broad definition of cycle paths
Bicycle routing
- BRouter - routing for cyclists with different profiles, on mobile or online (world-wide)
- Geovelo - routing for cyclists with different profiles, on mobile or online (Europe and North America)
- CycleStreets - routing for cyclists (UK, much of Europe, various cities around the world)
- BBBike @ World - a cycle route planner for more than 200 cities worldwide
- cycle.travel - routing for cyclists (UK, Europe, North America, Australia+NZ)
- GraphHopper - routing for cyclists (world-wide)
- Komoot - routing for cycling and hiking (world-wide)
- Naviki - routing for cyclists (world-wide)
- Trip4YouMaps [1] - routing, navigation & tracking for cycling and hiking (world-wide)
- Traili - routing for cyclists (world-wide)
See also
- sport=cycling
- cycleway:lane=* for marking distinction between advisory and exclusive bicycle lanes
- Proposal:Key:is sidepath - To indicate whether a cycle way runs in parallel along a street, making it adjoining or runs separated and thus detached from the road.
- DE:Bicycle(de) - big "portal" related to bicycle mapping (in German)
- Mountainbike - portal for mountainbiking
- Tourism - Cycling is a way for tourism.